How To Decrease Inode Usage In cPanel?
How To Decrease Inode Usage In cPanel?
When using a cPanel-managed server to manage your website, Inode usage can become a critical factor in efficiently managing your resources. An inode is a data structure a filesystem uses to store information about a file and a folder. It indicates the number of files and directories your website has on the hosting account.
When you have high inode usage on your account, it can lead to several issues, such as the inability to create new files or receive emails, or it can cause an account suspension in severe cases.
In this article, we will guide you through practical steps for decreasing inode usage in your cPanel account that ensures optimal performance & resource utilization of your hosting account.
Also Read: How To Upload Website Files and Database Using cPanel
Understanding Inode Usage
Before we delve into the solutions, It is important to understand the way of calculation for inode usage and its implications:
➢ Inode Count: Your each file in the hosting account, such as a document, image, email, and directory uses one inode.
➢ Limits: Your hosting provider sets inode limits for preventing a single user from consuming excessive resources because it could affect the performance of your server.
Also Read: How to Change PHP Version in cPanel?
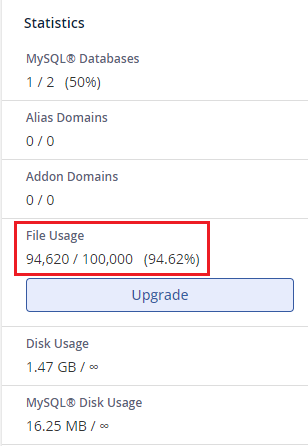
How to Check Inode Usage in cPanel
➢ Log in to your cPanel using your username and password.
➢ You will get the Inode Value in the ‘Statistics’ section on the right-hand side of the panel.
Know the Strategies to Decrease Inode Usage
Let’s find out the strategies to decrease inode usage in your hosting account.
1. Remove Unnecessary Files and Folders
➢ Delete Old Backups
We understand that backups are the most important factors for your website security and recovery, but they quickly consume a lot of space and inodes.
As we discussed above, each file in the backup counts towards the inode limit, so it is advisable to delete outdated or unnecessary backups from your account.
So, how will you manage these things?
Well, you need to regularly review your backup files and identify the outdated ones that are no longer necessary. You can consider the importance of each backup based on the data it includes and its relevance according to your current website state.
Once you have identified the backups no longer needed for your website, delete them from your hosting account. You can easily do this through the cPanel’s File Manager or any backup tool you are using.
If there is a case that you can’t delete any of the backups, we advise you to keep that data to an offsite storage solution like cloud storage services or you can buy a physical server. In this way, you can store your backups without using up the inode count of your hosting account.
Also Read: How to Create a PHPinfo File and View PHP Information?
➢ Clearing Cache Files
If you are using any CMS like WordPress, Joomla, etc, you need to clear cache directories as they generate a large number of files. These cache files can rapidly consume a large number of inodes.
You need to manage those files by implementing a regular schedule to clear them out. Many CMS platforms offer plugins or built-in tools for automating this process.
If your CMS does not automatically handle cache purging, the other way is you need to delete old cache files manually. You can do this process through the cPanel’s File Manager. You will see the separate cache folder in the main directory.
Along with this, it is advisable to configure your caching plugin or module settings for optimizing your cache lifecycle, which involves setting reasonable intervals for cache generation and expiration for minimizing inode usage without sacrificing the website’s performance.
Also Read: How to Clear the Website Cache in cPanel?
➢ Removing Unused Files/Folders
Over usage time, your website can gather various unused files, images, plugins, or themes contributing to your inode count, even if they are not actively used by your website.
In such cases, you need to manage your unused files or folders by auditing your website and periodically reviewing its files and directories. You need to look for old images, outdated plugins, themes, or other files that are no longer used.
It is advisable to delete the files carefully and always backup your website before removing plugins or themes to avoid accidental data loss or any functionality issues.
Also Read: How to Find the Missing htaccess File?
2. Optimize Your Email Usage
➢ Clear Old Emails
Your emails can consume a significant number of inodes. Regularly reviewing and deleting emails that are no longer needed is important.
For this, you must often look your emails in the trash folder, which are often overlooked by people but continue to consume resources. You need to regularly empty the trash folder, which can recover considerable inode usage.
You also need to look for spam emails that accumulate inode quickly and in large numbers and clear out the spam folder to prevent unnecessary inode usage.
Along with spam and trash, don’t forget to consider the emails present in your inbox and other folders. If it is possible, deleting old or irrelevant emails can significantly reduce inode consumption.
Also Read: How to Take Backup of Emails from cPanel
➢ Archive Your Emails
If deleting emails is not possible, you can retain them by archiving them. This process involves moving them from your server to the local computer. It decreases inode usage on the server while keeping your emails accessible offline.
You can do this by manually archiving your emails with email clients like Outlook and Thunderbird, which offer the option to save emails to your computer.
You can also do this by automating the process, as some email clients & third-party tools offer automated archiving solutions. It periodically archives emails based on certain criteria, such as email age, sender, or email size.
Also Read: How to Create a Catchall Email Address in cPanel?
Conclusion
By implementing the strategies outlined above, you can effectively reduce inode usage, ensure that your website runs smoothly, and maintain the health and performance of your hosting account.
Related Posts:
- How to Enable or Disable PHP Error Logging in cPanel?
- How to Create a basic SPF Record in cPanel?
- How To Decrease Inode Usage In cPanel?
- How to Reset Email Account Password in cPanel?
- How to Create a Table in phpMyAdmin?
- How to Change MySQL Database User Password From cPanel?
- How to Configure Domain Redirects in cPanel?
- How to Change Table Name in phpMyAdmin?
- How to Set up Email Forwarding in cPanel?
- How to Change the Time Zone in cPanel Roundcube Webmail?
Latest Posts
- Server-Side Scripting: PHP, Node.js, Python – A Detailed Comparison
- Securing Your Website in 2024: Essential Strategies for Online Safety
- The Future of Web Development Technologies: Trends to Watch in 2024
- How Banks Handle Server-Side Operations and Ensure System Security: An Inside Look
- Tips for Writing Clean, Understandable, and Efficient Code: Avoiding Garbage Code
- Tailwind CSS: Revolutionizing Modern Web Design
- Basic Linux Commands for Beginners: A Starter Guide
- Dairy Farming Loan Apply
- BSNL Recharge Plan
- Bijli Bill Mafi Yojana Online Apply
Technical
- DevOps Roadmap
- How To Install and Configure an SNMP on Ubuntu 20.04
- Apple releases iOS 18 Developer Beta 2 with iPhone screen mirroring, RCS toggle,and more
- How to enable SNMP on Ubuntu Linux 18.04 and above
- How to Force HTTPS Using .htaccess (Updated 2024)
- Display All PHP Errors: Basic & Advanced Usage
- PHP alert
- MongoDB loads but breaks, returning status=14
- MongoDB database deleted automatically
- MongoDB all Error Solutions
Category
